The alkali metals
The alkali metals are the reactive elements in group 1 of the Periodic Table: Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb), Caesium (Cs) and Francium (Fr).
Reactions with oxygen
The alkali metals are soft, shiny metals which react immediately with oxygen in the air - they tarnish or corrode forming a layer of the metal oxide on the surface. They need to be stored under oil (Usually paraffin). They burn readily in oxygen. For example:
Lithium + Oxygen > Lithium oxide
4Li + O2 > 2Li2O
The other alkali metals react in a similar way, and the reactions become progressively more violent down the group.
Reactions with water
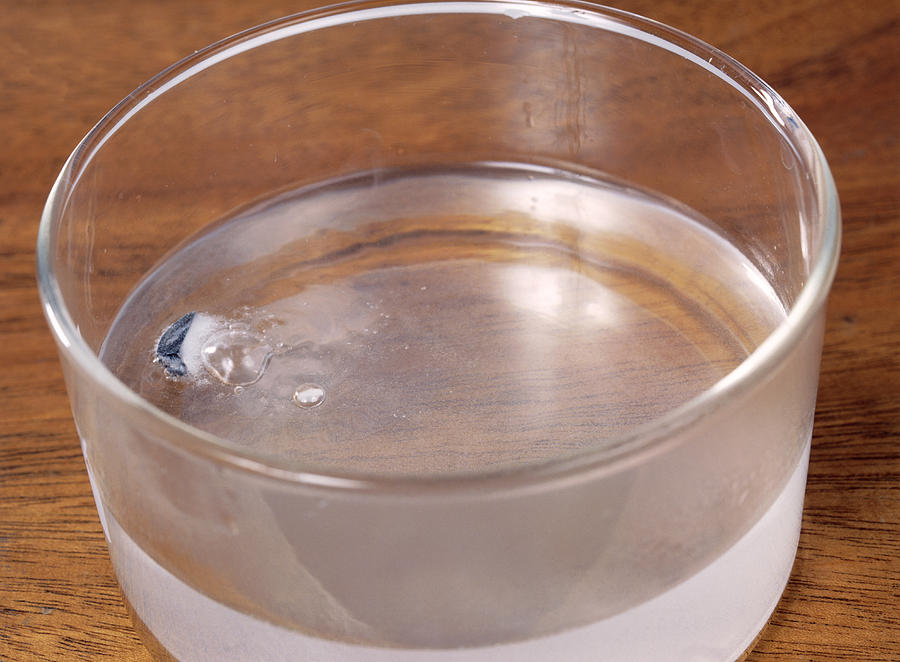
The alkali metals react vigorously with water. Lithium fizzes on contact with water, forming the alkali lithium hydroxide (LiOH) along with bubbles of hydrogen (H2) gas.
Lithium + water > Lithium hydroxide + hydrogen
2Li + 2H2O > 2Li2O + H2
^ Lithium metal reacting with water
The other alkali metals react in a similar way, and the reactions become progressively more violent down the group. Sodium fizzes violently, potassium creates so much heat as it reacts with the water that it ignites the hydrogen gas produced, producing a lilac color flame. the other alkali metals react so violently that it is not safe to carry out the reactions within a school lab.
Reactions with halogens
'The halogens' is the same name given to the group 7 elements of the periodic table, including fluorine and chlorine.
Lithium reacts (burns) readily in chlorine gas, producing a salt called lithium chloride (LiCl).
Lithium + Chlorine > Lithium chloride
2Li + Cl2 > 2LiCl
Lithium reacts with bromine in a very similar way, forming lithium bromide.
The other alkali metals react similarly, and again the reactions become progressively more violent down the group.
The reactions of the alkali metals with oxygen, with water and with the halogens show us that the reactivity of the alkali metals increases down the group. The least reactive metal in lithium, and the most reactive is francium. Potassium is the most reactive alkali metal allowed in schools.
Flame tests
Alkali metals present in compounds such as lithium chloride, sodium bromide or potassium sulfate, can be identified by strongly heating a sample in a roaring Bunsen burner flame and noting the color observed.
- Lithium compounds burn with a red colored flame
- Sodium compounds burn with a yellow / orange colored flame
- Potassium compounds produce a lilac colored flame.
^ Lithium compounds burn red in a Bunsen flame


No comments:
Post a Comment